قاجار خاندان
دولت علیہ ایران Sublime State of Persia دولت علیّه ایران Dowlat-e Elliye ye Irān | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1785–1925 | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
ترانہ: سلامتی شاہ | |||||||||||||||||
 انیویں صدی وچ فارس قاجار خاندان دے تحت | |||||||||||||||||
| حیثیت | سلطنت | ||||||||||||||||
| دار الحکومت | تہران | ||||||||||||||||
| عام زباناں | فارسی (عدالت ادب، انتظامی، ثقافتی، سرکاری)،[۱][۲] ترکی (عدالت زبان تے مادری زبان)[۳] | ||||||||||||||||
| حکومت | مطلق شہنشاہیت (1785–1906) آئینی بادشاہت (1906–1925) | ||||||||||||||||
| شاہ، مرزا | |||||||||||||||||
• 1794–1797 | محمد خان قاجار (اول) | ||||||||||||||||
• 1909–1925 | احمد شاہ قاجار (آخر) | ||||||||||||||||
| وزیر اعظم | |||||||||||||||||
• 1906 | مرزا نصر اللہ خان (اول) | ||||||||||||||||
• 1923–1925 | رضا شاہ پہلوی (آخر) | ||||||||||||||||
| تاریخ | |||||||||||||||||
• آغاز قاجار خاندان | 1785 | ||||||||||||||||
• معاہدہ گلستان | 1813 | ||||||||||||||||
• معاہدہ ترکمناچی | 1828 | ||||||||||||||||
• معاہدہ پریس | 1857 | ||||||||||||||||
• معاہدہ اخال | 1881 | ||||||||||||||||
• آغاز پہلوی کاندان | 1925 | ||||||||||||||||
| کرنسی | تومان | ||||||||||||||||
| آیزو 3166 رمز | [[آیزو 3166-2:|]] | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| موجودہ حصہ | |||||||||||||||||
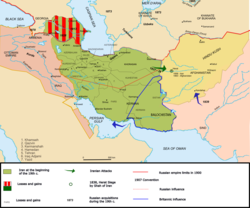
قاجار خاندان (Qajar dynasty) (![]() قاجار (help·info)) (فارسی: دودمان قاجار) اک ترک النسل [۴][۵][۶][۷][۸] ایرانی شاہی خاندان سی، جس نے 1785ء توں 1925ء تک فارس (ایران) اُتے حکومت دی۔ [۹][۱۰]
قاجار خاندان نے 1794ء وچ زند خاندان دے آخری حکمران لطفعلی خان زند نوں شکست دے کے فارس دا مکمل کنٹرول حاصل کر لیا، تے قفقاز تے وسطی ایشیاء دے وڈے حصےآں اُتے فارسی خودمختاری دوبارہ قائم دی۔ 1796ء وچ محمد خان قاجار نے آسانی دے نال مشہد اُتے قبضہ کر لیا جو اس وقت درانی سلطنت دے تحت سی۔ [۱۱]
قاجار (help·info)) (فارسی: دودمان قاجار) اک ترک النسل [۴][۵][۶][۷][۸] ایرانی شاہی خاندان سی، جس نے 1785ء توں 1925ء تک فارس (ایران) اُتے حکومت دی۔ [۹][۱۰]
قاجار خاندان نے 1794ء وچ زند خاندان دے آخری حکمران لطفعلی خان زند نوں شکست دے کے فارس دا مکمل کنٹرول حاصل کر لیا، تے قفقاز تے وسطی ایشیاء دے وڈے حصےآں اُتے فارسی خودمختاری دوبارہ قائم دی۔ 1796ء وچ محمد خان قاجار نے آسانی دے نال مشہد اُتے قبضہ کر لیا جو اس وقت درانی سلطنت دے تحت سی۔ [۱۱]
شاہان فارس، 1794–1925 سودھو
| ناں | تصویر | خطاب | پیدائش-وفات | آغاز دور | اختتام دور | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | محمد خان قاجار | 
|
شہنشاہ | 1742–1797 | 20 مارچ 1794 | 17 جون 1797 |
| 2 | فتح علی شاہ قاجار | 
|
شہنشاہ | 1772–1834 | 17 جون 1797 | 23 اکتوبر 1834 |
| 3 | محمد شاہ قاجار | 
|
شاہ | 1808–1848 | 23 اکتوبر 1834 | 5 ستمبر 1848 |
| 4 | ناصر الدین شاہ قاجار | 
|
شہنشاہ | 1831–1896 | 5 ستمبر 1848 | 1 مئی 1896 |
| 5 | مظفر الدین شاہ قاجار | 
|
شہنشاہ تے سلطان | 1853–1907 | 1 مئی 1896 | 3 جنوری 1907 |
| 6 | محمد علی شاہ قاجار | 
|
شہنشاہ | 1872–1925 | 3 جنوری 1907 | 16 جولائی 1909 |
| 7 | احمد شاہ قاجار | 
|
سلطان | 1898–1930 | 16 جولائی 1909 | 15 دسمبر 1925 |
حوالے سودھو
- ↑ Homa Katouzian, "State and Society in Iran: The Eclipse of the Qajars and the Emergence of the Pahlavis"، Published by I.B.Tauris, 2006. pg 327: "In post-Islamic times, the mother-tongue of Iran's rulers was often Turkic, but Persian was almost invariably the cultural and administrative language"
- ↑ Homa Katouzian, "Iranian history and politics"، Published by Routledge, 2003. pg 128: "Indeed, since the formation of the Ghaznavids state in the tenth century until the fall of Qajars at the beginning of the twentieth century, most parts of the Iranian cultural regions were ruled by Turkic-speaking dynasties most of the time. At the same time, the official language was Persian, the court literature was in Persian, and most of the chancellors, ministers, and mandarins were Persian speakers of the highest learning and ability"
- ↑ Turkic-Iranian Contacts، John R. Perry, Encyclopaedia Iranica، (اگست 15, 2006);"Turkic was also the mother tongue and, to an extent, the court language of the subsequent Afsharid and Qajar dynasties"۔[۱]
- ↑ Lua error in ماڈیول:Citation/CS1/ar at line 3440: attempt to call field 'set_selected_modules' (a nil value).
- ↑ Cyrus Ghani. Iran and the Rise of the Reza Shah: From Qajar Collapse to Pahlavi Power، I.B. Tauris, 2000, ISBN 1-86064-629-8, p. 1
- ↑ William Bayne Fisher. Cambridge History of Iran، Cambridge University Press, 1993, p. 344, ISBN 0-521-20094-6
- ↑ Dr Parviz Kambin, A History of the Iranian Plateau: Rise and Fall of an Empire, Universe, 2011, p.36, online edition۔
- ↑ Jamie Stokes, Anthony Gorman, Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Africa and the Middle East, 2010, p.707, Online Edition، The Safavid and Qajar dynasties, rulers in Iran from 1501 to 1722 and from 1795 to 1925 respectively, were Turkic in origin.
- ↑ Abbas Amanat, The Pivot of the Universe: Nasir Al-Din Shah Qajar and the Iranian Monarchy, 1831–1896, I.B.Tauris, pp 2–3; "In the 126 years between the fall of the Safavid state in 1722 and the accession of Nasir al-Din Shah, the Qajars evolved from a shepherd-warrior tribe with strongholds in northern Iran into a Persian dynasty.۔"
- ↑ Choueiri, Youssef M.، A companion to the history of the Middle East، (Blackwell Ltd.، 2005)، 231,516.
- ↑ (1981) Muslim World. Brill Archive, 65, 370. ISBN 978-90-04-06196-5. Retrieved on 28 ستمبر 2012.

